Introduction
Email is a critical communication tool for businesses, and its reliability depends heavily on the Domain Name System (DNS). If DNS settings are incorrect, emails might never reach their destination, causing disruptions and potential revenue loss. This article explores the top seven common DNS errors that cause email delivery failures and explains how to fix DNS errors with clear solutions. Let’s explore how you can ensure your emails reach the right inbox without getting lost in cyberspace.
What is DNS and How Does it Affect Email Delivery?
Understanding DNS Basics
DNS stands for Domain Name System, a vital component of the internet that acts like a phonebook. It translates familiar domain names like “example.com” into numerical IP addresses that computers rely on for communication. Without DNS, navigating the web and sending emails would be far more complex, relying solely on numeric IPs.
The Connection Between DNS and Email Systems
DNS is essential for effective email delivery. Email servers rely on DNS to locate the recipient’s server. If the DNS records are misconfigured or incorrect, the email may bounce back, get lost, or land in the spam folder. Accurate DNS settings are crucial for the seamless operation of any email system.
Common DNS Errors That Lead to Email Failures
1. Incorrect MX Records
What Are MX Records?
MX (Mail Exchange) records route emails to the correct email server. They determine where the email sent to your domain should be delivered. If these records are not set up correctly, incoming emails will fail to reach your mailbox.
How Incorrect MX Records Affect Email Delivery
When MX records are incorrect, email servers may not be able to find the right destination for your messages. This can lead to undelivered emails, increased bounce rates, and possible blacklisting of your domain due to poor email reputation.
How to Fix Incorrect MX Records
To fix incorrect MX records, follow these steps:
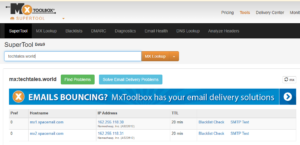
- Navigate to your DNS management dashboard, which is available through your domain registrar or DNS hosting provider.
- Check the MX records for your domain. Ensure they point to the correct mail server and use the correct priority values.
- Update any incorrect records, save changes, and allow a few minutes for the changes to take effect.
- Test your MX configuration using online tools like MXToolbox to ensure emails route correctly.
Read more on how to use MXToolbox to find MX Record errors and fixes
2. Missing or Misconfigured SPF Records
What Are SPF Records?
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is a DNS record that identifies which servers are allowed to send emails for your domain. It’s an important part of email authentication to prevent spoofing and ensure deliverability.
How Missing SPF Records Impact Deliverability
Without proper SPF records, receiving email servers might reject or mark your emails as spam. This impacts your email’s trustworthiness and can damage your domain’s sending reputation.
How to Fix SPF Record Issues
Here’s how to address SPF problems:
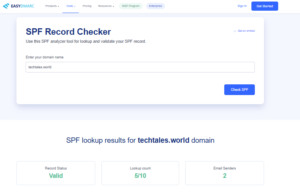
- Verify if your domain has an SPF record using DNS lookup tools like MXToolbox
- Create an SPF record in your DNS management if one doesn’t exist. The basic syntax is:
(Replace “_spf.google.com” with the server you’re authorizing).
- Test the SPF configuration using tools like SPF Record Checkers.
- Adjust the SPF policy to ensure it’s aligned with your email sending practices.
3. Invalid DKIM Configuration
What Is DKIM?
DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) is an authentication method that adds a digital signature to your emails, verifying that the email was sent from an authorized server and hasn’t been tampered with during transmission.
How Invalid DKIM Affects Emails
Invalid DKIM configurations lead to authentication failures, making it more likely for your emails to be marked as spam or rejected entirely by the recipient’s server. A correct DKIM setup is crucial for maintaining your email’s integrity.
How to Fix DKIM Configuration Errors
To ensure proper DKIM setup:
- Create a DKIM key pair—consisting of a public and private key—using your email service provider.
- Publish the public key in your DNS records under a specific TXT record.
- Set your email server to sign outgoing emails using the private keys.
- Use DKIM testing tools to verify that emails are being signed correctly and pass authentication checks.
Any of the tools that we mentioned above(MX Toolbox, Easy DMARC etc.) can be used to verify the DKIM records.
Read more on how to use MX Toolbox to verify all the DNS records.
4. DNS Lookup Timeouts
What is a DNS Lookup Timeout?
A DNS lookup timeout happens when an email server tries to perform a DNS query, but the DNS server fails to respond within the expected timeframe. Problems with these settings can cause email delays or even failed deliveries.
Causes of DNS Lookup Timeouts
Several factors can lead to timeouts:
- Slow or overloaded DNS servers
- Misconfigured DNS settings
- These issues might stem from the DNS resolver or network connection problems.
How to Address DNS Lookup Timeout Errors
To reduce DNS timeouts:
- Switch to a reliable DNS provider that ensures faster query responses.
- Reduce DNS lookups by streamlining your email’s DNS dependencies.
- Optimize your DNS server settings to improve query speed.
- Monitor DNS server performance to identify bottlenecks or network issues.
5. Missing or Incorrect DMARC Records
What Is DMARC?
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) helps domain owners protect their domain from unauthorized use, such as email spoofing. It builds on SPF and DKIM to provide an additional layer of security.
Consequences of Missing or Incorrect DMARC Records
If DMARC records are missing or misconfigured, your domain’s emails are more susceptible to phishing and spoofing attacks. It can also lead to deliverability issues if receiving servers can’t verify your emails’ legitimacy.
How to Correct DMARC Record Errors
To implement and verify a DMARC policy:
- Create a DMARC TXT record in your DNS configuration with appropriate settings. Example:
- Choose a policy that matches your needs:
none,quarantine, orreject. - Test the DMARC setup using a DMARC checker tool like MX Toolbox.
- Adjust policies as needed based on the DMARC reports you receive.
If you are not sure about the DMARC value to be given, you can contact your email provider’s technical support and they will provide the exact value to be entered.
6. DNS Propagation Delays
What is DNS Propagation?
DNS propagation refers to the time it takes for DNS changes to spread and update across the entire global network of DNS servers. When you make changes to your DNS records, such as updating an MX or SPF record, it can take up to 48 hours for these changes to propagate worldwide.
How DNS Propagation Delays Impact Email Delivery
During DNS propagation, outdated information may be cached by some DNS servers, causing emails to route incorrectly or fail to deliver. This can lead to email bounces, lost messages, or delays as some servers use old DNS data before updating.
Steps to Mitigate DNS Propagation Delays
To reduce the impact of propagation delays:
- Lower the TTL (Time to Live) value of your DNS records before making changes. A shorter TTL (e.g., 300 seconds) forces DNS servers to refresh the records more frequently.
- Schedule DNS updates during periods of low email traffic to minimize potential disruptions.
- Use DNS monitoring tools to check which DNS servers have updated and identify those still showing old information.
- Avoid making multiple changes in a short period, as this can increase confusion during the propagation process.
7. Reverse DNS (PTR Record) Errors
What Is Reverse DNS (rDNS)?
IP addresses are linked to domain names via reverse DNS (rDNS). This involves PTR (Pointer) records, which are the opposite of regular DNS records. Email servers use rDNS to verify that an IP address matches the domain it claims to be sending from, which is crucial for spam filtering and authentication.
Impact of Incorrect rDNS on Email Delivery
If the rDNS is incorrect or missing, emails may be flagged as spam or rejected by the recipient’s email server. Many ISPs and corporate email systems rely on proper rDNS configurations to validate legitimate email traffic.
How to Resolve Reverse DNS Errors
To correct rDNS issues:
- Make sure the PTR record for your email server’s IP address is set up or updated with your hosting provider or Internet service provider.
- Ensure the PTR record correctly points to your domain name (e.g., mail.yourdomain.com).
- Test the rDNS setup using tools like
nslookupor online rDNS checking tools to confirm the configuration. - Monitor spam reports and email bounces to ensure the rDNS change improves deliverability.
Best Practices for Preventing DNS-Related Email Failures
Regular DNS Audits and Monitoring
To ensure your email system runs smoothly, conducting regular DNS audits is essential. A DNS audit helps identify outdated or misconfigured records that might cause email issues. Use DNS monitoring tools to set alerts for any unexpected changes or issues in your DNS settings.
Tips for Effective DNS Monitoring:
- Use automated tools like DNSChecker or MXToolbox to monitor DNS health.
- Schedule quarterly or bi-annual DNS audits to verify the accuracy of records.
- Implement email logs to track delivery issues and identify patterns linked to DNS errors.
Using Reliable DNS Hosting Providers
Not all DNS hosting providers are created equal. Choosing a reliable DNS hosting provider can make a significant difference in your email deliverability and domain security. Premium DNS providers offer additional features like faster DNS resolution, robust security, and better uptime guarantees.
- High uptime (99.99% or higher) for reliability.
- Support for a variety of DNS configurations at advanced levels, including DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions).
- Fast DNS resolution times to minimize lookup delays.
- Easy-to-use management interface for record updates.
Keeping DNS Records Updated
Outdated DNS records can cause delivery failures as email servers may rely on stale information. Keep your DNS records up to date, especially if you’ve made changes to your hosting, email provider, or domain setup.
Best Practices:
- Set reminders for periodic DNS checks.
- Immediately update DNS records when switching email services or hosting.
- Ensure that changes are accurately reflected in SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records.
Tools to Diagnose and Fix DNS Issues
Effective tools can simplify DNS management and troubleshooting. Below are some recommended tools for diagnosing and resolving DNS-related email problems:
DNS Lookup Tools
- MXToolbox: Offers comprehensive DNS lookups, including MX, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records.
- DNSChecker: Provides global DNS propagation checks to see how DNS changes are progressing.
- WhatsMyDNS: Another tool for checking the status of DNS propagation across different servers.
Email Authentication Testing Tools
- DMARC Analyzer: Helps verify DMARC setup and track DMARC compliance.
- SPF Record Checker: Allows you to inspect your SPF record to ensure it’s properly configured.
- DKIM Validator: Checks DKIM configuration and helps troubleshoot issues related to email signing.
Comprehensive DNS Management Platforms
- Cloudflare DNS: Known for its user-friendly interface, security features, and fast DNS resolution.
- Google Cloud DNS: Offers scalable DNS management with excellent performance.
- Amazon Route 53: Provides robust DNS services with advanced routing options and high availability.
Conclusion
DNS errors can severely impact email deliverability, disrupting communication and business operations. Understanding common DNS issues like incorrect MX records, missing SPF or DKIM configurations, DNS lookup timeouts, and more can help you troubleshoot and fix problems before they escalate. By following best practices, regularly auditing DNS, and using reliable tools, you can maintain a healthy DNS environment that ensures your emails reach their intended destination.
Maintaining a well-configured DNS setup isn’t just about sending emails—it’s about safeguarding your business’s reputation, ensuring smooth communication, and avoiding potential security threats.
FAQs
- What happens if my MX records are set up incorrectly? Incorrect MX records can prevent your email server from receiving emails. Messages sent to your domain might bounce back, be delayed, or get lost entirely, disrupting your communication.
- How often should I check my DNS records? It’s best to audit your DNS records every 3 to 6 months. However, if you make significant changes to your hosting or email service, update and review them immediately.
- Can DNS issues affect other online services besides email? Yes, DNS issues can affect your website’s accessibility, performance, and security, as well as any other online service tied to your domain, such as VoIP or databases.
- What is the best way to test if my DNS is working correctly? Use online tools like MX Toolbox or DNS Checker to conduct a full DNS lookup. These tools can help you check MX, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records to ensure everything is configured properly.
- Is it necessary to have a DMARC record? Yes, a DMARC record is crucial for protecting your domain from email spoofing and improving email deliverability. It ensures that your SPF and DKIM configurations are correctly enforced and provides feedback on any authentication failures.
Read more, MX Toolbox: Quickly Resolve Email Issues with Powerful DNS Diagnostic Tools


Leave a Reply