Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
In today’s fast-evolving IT landscape, managing devices, applications, and security efficiently is a top priority for businesses. Enter Microsoft Intune, a powerful cloud-based tool that offers modern solutions for device and application management. Intune allows organizations to maintain secure access to corporate resources, enforce compliance, and provide seamless user experiences—all without the need for complex on-premises infrastructure.
Let’s dive into the essentials of Microsoft Intune, how it works, and why it’s become a cornerstone for modern enterprise IT management.
1. What is Microsoft Intune?
Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based service that facilitates mobile device management (MDM) and mobile application management (MAM). Designed for modern workplaces, Intune enables IT administrators to secure devices and applications across a diverse range of platforms, including Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android.
As part of Microsoft’s Endpoint Manager ecosystem, Intune integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft tools like Azure Active Directory and Microsoft 365, making it a holistic solution for enterprise device management.
2. Key Features of Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Intune’s feature set is extensive, catering to modern businesses with diverse IT needs. Key features include:
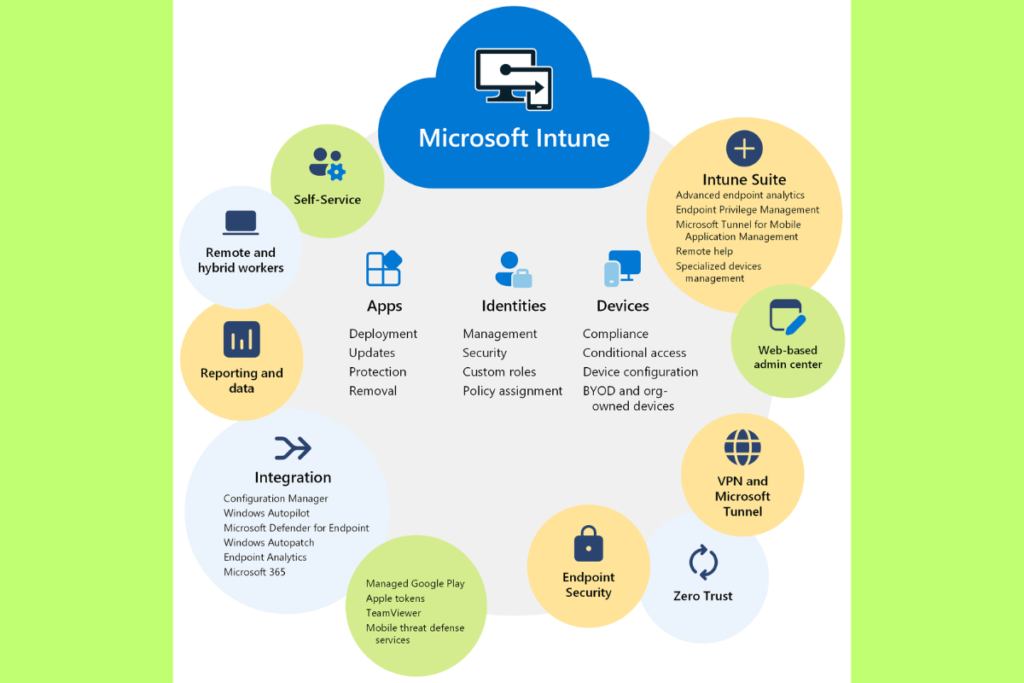
- Device Management: Enroll and manage a wide range of devices across different platforms.
- Application Management: Control access to corporate apps while ensuring data security.
- Conditional Access: Enforce access policies based on compliance and security configurations.
- Compliance Policies: Define rules to ensure devices meet organizational standards.
- Zero-Touch Deployment: Configure devices remotely without user intervention.
- Integration with Azure AD: Simplified authentication and single sign-on.
- Endpoint Security: Strengthen device protection against cybersecurity threats.
3. Benefits of Using Microsoft Intune
Why should businesses consider implementing Intune? Here’s a breakdown of its advantages:
- Enhanced Security: Protect corporate data with robust policies, encryption, and conditional access.
- Simplified IT Management: Streamline administrative tasks through centralized dashboards.
- Scalability: Easily manage devices and users across multiple locations.
- Cost-Efficiency: Eliminate the need for expensive on-premises infrastructure.
- BYOD Support: Manage personal devices without compromising security.
- User Productivity: Provide employees with secure, uninterrupted access to tools and applications.
4. Microsoft Intune vs Traditional Device Management
Traditional device management relied heavily on on-premises servers, manual configurations, and rigid deployment models. Microsoft Intune, however, revolutionizes the process with its:
- Cloud-Based Management: Eliminate physical infrastructure.
- Cross-Platform Support: Manage Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android devices.
- Advanced Analytics: Leverage AI insights for proactive management.
- Automation: Simplify deployment and compliance enforcement.
5. How Microsoft Intune Works
Microsoft Intune operates through a cloud-native architecture, where devices and users are managed via a secure web-based portal. Its workflow typically involves:
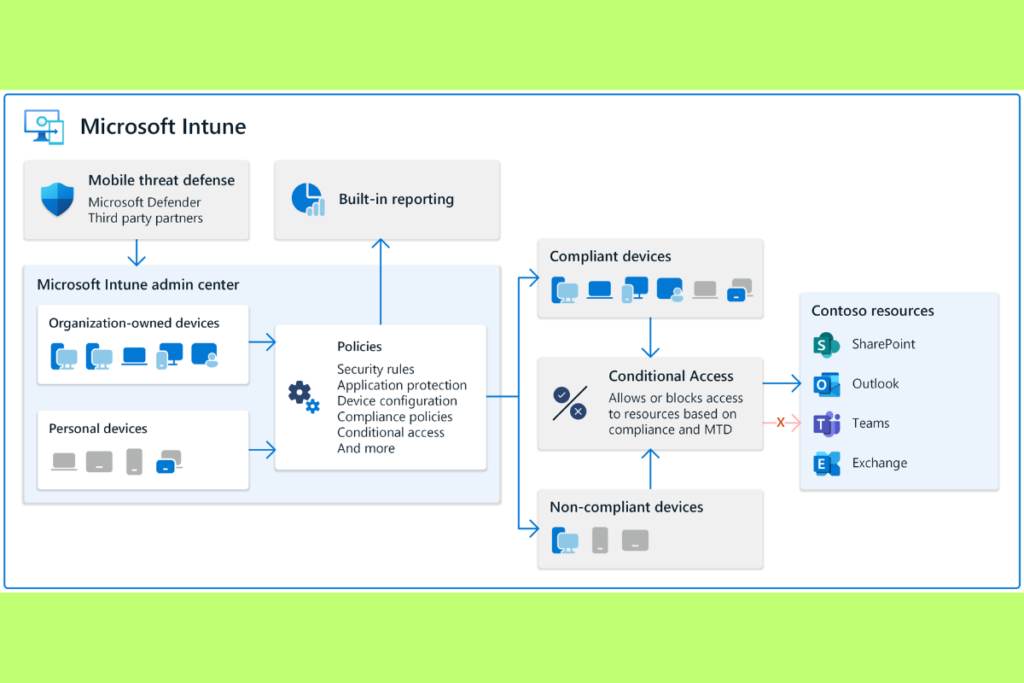
- Enrollment: Devices are registered to the Intune service via self-service or IT-initiated methods.
- Policy Application: IT admins deploy compliance and security policies to ensure adherence to company standards.
- App Distribution: Distribute, monitor, and control access to corporate apps.
- Monitoring: Use dashboards and analytics to oversee device health, compliance, and performance.
6. Integrating Intune with Microsoft Endpoint Manager
Intune is a core component of the Microsoft Endpoint Manager suite, which combines Intune and Configuration Manager for a unified management experience.
- Benefits of Integration:
- Unified endpoint security and management.
- Support for both on-premises and cloud-based devices.
- Simplified migration paths for hybrid IT environments.
7. Device Enrollment in Microsoft Intune
Device enrollment is the first step toward successful Intune implementation. Organizations can choose from several enrollment methods:
- Self-Service Enrollment: Users register their devices via a portal or app.
- Autopilot: Automate Windows device setup and configuration.
- Apple Business Manager: Enroll Apple devices seamlessly.
8. Managing BYOD with Intune
The rise of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies has made tools like Intune indispensable. Intune supports BYOD strategies by:
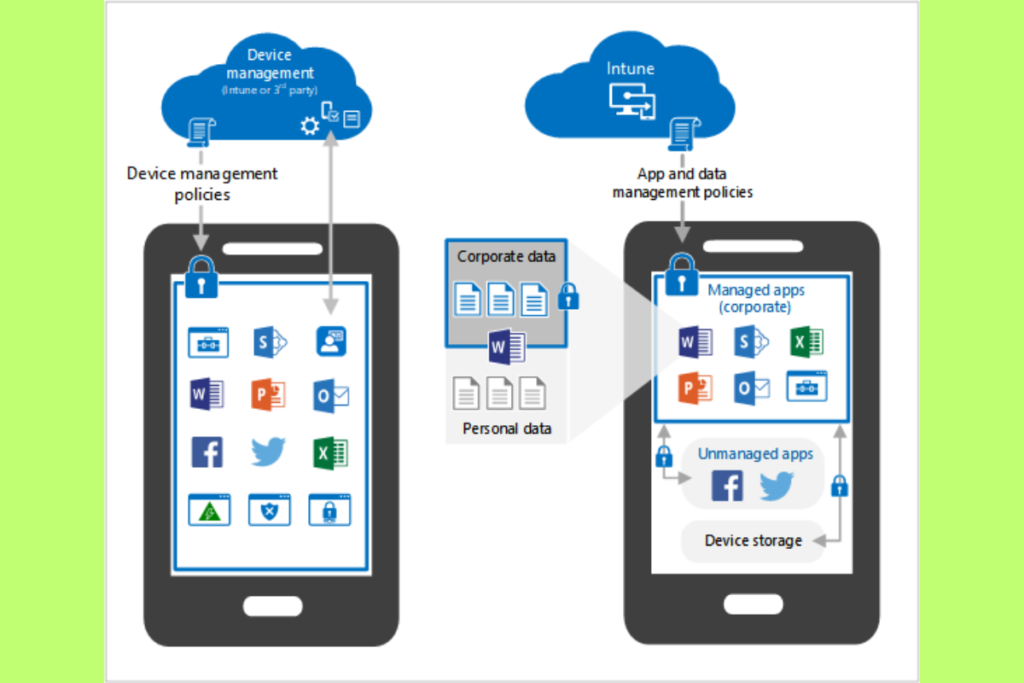
- Segregating personal and corporate data.
- Allowing remote wipe of corporate information without affecting personal files.
- Enabling secure access to apps and resources on personal devices.
9. Application Management Through Intune
Mobile Application Management (MAM) is another core feature of Intune. Key aspects include:
- Restricting app usage based on compliance.
- Protecting sensitive data with app-level policies.
- Controlling app installations and updates.
10. Intune’s Role in Endpoint Security
In today’s threat-heavy landscape, Microsoft Intune provides robust endpoint security features, including:
- Threat Detection: Integration with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
- Conditional Access: Block access from non-compliant devices.
- Encryption Enforcement: Require BitLocker or FileVault for data protection.
11. Intune Pricing and Licensing Options
Microsoft Intune offers flexible pricing plans tailored to meet the needs of organizations of varying sizes. It’s available as a standalone product or as part of the Microsoft 365 and Enterprise Mobility + Security (EMS) suites.
- Standalone Intune: Ideal for businesses focused on device and app management without the need for additional Microsoft services.
- Microsoft 365 Plans: Includes Intune as part of comprehensive business productivity and security solutions.
- EMS Suite: Combines Intune with Azure Active Directory, Azure Information Protection, and Advanced Threat Analytics.
Prices depend on the features included, with affordable per-user, per-month pricing models. Check the prices here.
12. The Future of Microsoft Intune
Microsoft continues to enhance Intune with new features and integrations. The future of Intune is focused on:
- AI-Driven Management: Leveraging artificial intelligence to predict and resolve device issues proactively.
- Stronger Integrations: Expanding compatibility with third-party applications and tools.
- Sustainability Goals: Supporting green IT initiatives through energy-efficient device management.
How to Set Up Microsoft Intune
Setting up Microsoft Intune can seem overwhelming at first, but with a clear step-by-step approach, even beginners can successfully implement this powerful device management tool. Intune simplifies modern IT management, making it easier to secure devices, applications, and data. Let us go through the setup process, helping you take the first steps in using Intune to protect your organization’s digital assets.
Prerequisites for Setting Up Microsoft Intune
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
- Microsoft Intune License: Purchase Intune as a standalone license or as part of Microsoft 365 or the Enterprise Mobility + Security (EMS) suite.
- Global Admin Role: You need administrative rights in your organization’s Microsoft 365 or Azure account.
- Azure Active Directory (Azure AD): Devices and users must be registered in Azure AD for Intune management.
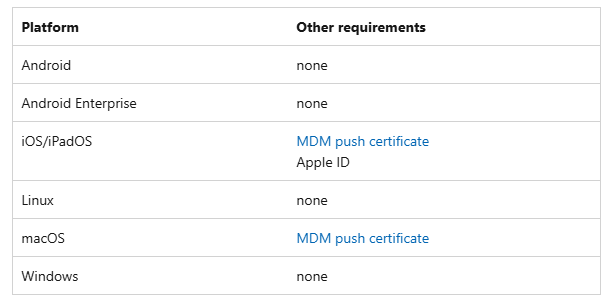
- Compatible Devices: Verify that the devices you plan to manage meet Intune’s compatibility requirements.
- Access to the Microsoft Endpoint Manager Admin Center: This is where all Intune configurations are done.
Device Compatibility:
Step 1: Accessing Microsoft Endpoint Manager
- Sign in to the Microsoft Endpoint Manager Admin Center using your Microsoft 365 credentials.
- Locate the Microsoft Intune section on the dashboard.
This portal serves as the control center for all your Intune configurations and management tasks.
Step 2: Set Up Basic Intune Configuration
1. Configure Tenant Settings
- Navigate to Tenant Administration in the left-hand menu.
- Set up custom branding (optional) for a personalized experience for your employees.
- Enable Device Enrollment to allow users to register devices.
2. Link Intune to Azure AD
- Ensure your organization’s users and devices are registered in Azure AD.
- Open the Azure Portal, navigate to Azure Active Directory > Devices to manage and review registered devices.
- Enable Device Registration if it’s not already active.
Step 3: Enroll Devices into Intune
Device Enrollment Methods
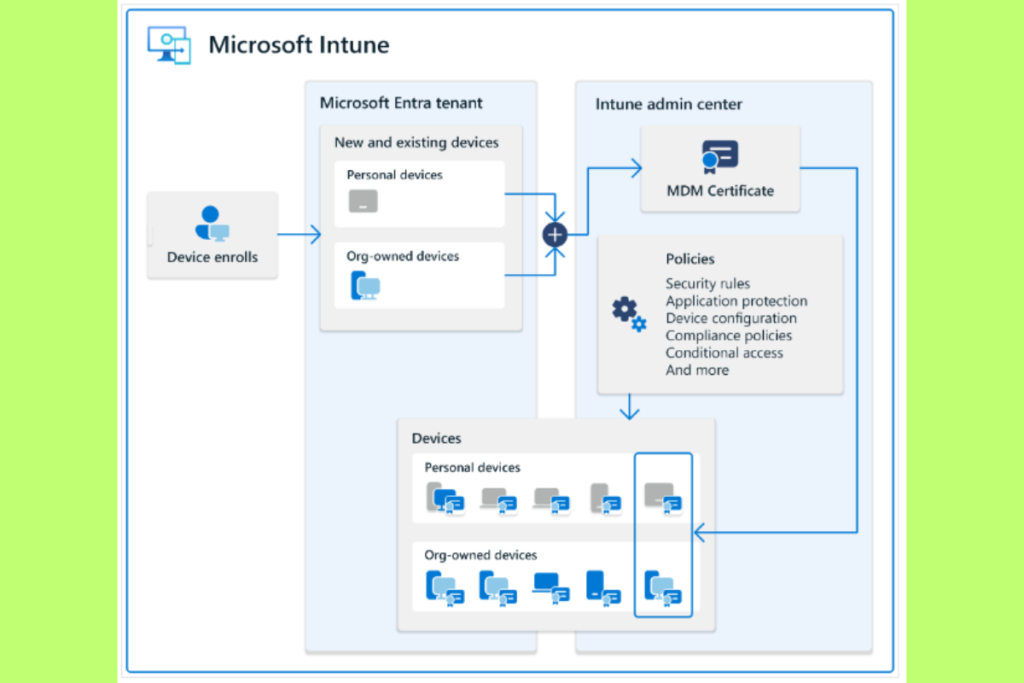
Microsoft Intune supports several enrollment methods depending on the type of device:
- For Windows Devices
- Use Windows Autopilot for zero-touch deployment of corporate-owned devices.
- For BYOD scenarios, enable self-service enrollment through the Company Portal App.
- For macOS Devices
- Integrate with Apple Business Manager (ABM) to streamline enrollment and app deployment.
- Alternatively, manually enroll macOS devices using configuration profiles.
- For iOS and iPad OS Devices
- Use Apple Enrollment via ABM or a direct connection.
- Install the Intune Company Portal App on the required devices to complete self-service enrollment.
- For Android Devices
- Choose Android Enterprise Enrollment for corporate-owned devices.
- Use BYOD Enrollment with the Intune app for personal devices.
Step 4: Create Compliance and Security Policies
- Define Compliance Standards
- In the Endpoint Manager Admin Center, go to Devices > Compliance Policies to configure and enforce device compliance rules.
- Create a new compliance policy for each device platform (Windows, iOS, macOS, Android).
- Specify rules such as password complexity, encryption, and device health requirements.
- Set Up Conditional Access
- Access Azure Active Directory > Security > Conditional Access to set up policies that control access based on compliance and security criteria.
- Create policies to enforce compliance before granting access to corporate resources.
- Enable Endpoint Security
- Use Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to enhance threat detection and response capabilities.
- Apply encryption policies such as BitLocker (Windows) or FileVault (macOS) for data protection.
Step 5: Deploy Apps and Resources
- Add and Assign Apps
- Navigate to Apps > All Apps in the Endpoint Manager portal.
- Select Add App, upload your app package (e.g., .msi, .apk), or connect to public app stores.
- Assign apps to specific user groups or devices.
- Distribute Certificates and Profiles
- Create configuration profiles to distribute Wi-Fi settings, VPN credentials, and email configurations.
- Use certificate profiles for secure access to enterprise resources.
- Push Updates
- Enable automated updates for managed devices to keep them current with the latest security patches and feature enhancements, ensuring optimal performance and protection against vulnerabilities.
Step 6: Monitor and Manage Devices
- Use Dashboards for Insights
- The Endpoint Manager Dashboard offers a snapshot of device compliance, app usage, and security risks.
- Drill down into specific devices or users to troubleshoot issues.
- Reports and Logs
- Generate detailed compliance reports to verify that devices meet your organization’s defined security and policy standards.
- Monitor logs for enrollment errors, security breaches, or app deployment issues.
- Remote Actions
- Perform actions such as remote wipe, reset, or lock directly from the Endpoint Manager portal.
Step 7: Test and Refine
- Pilot Testing: Start with a small group of users or devices to test your Intune configurations.
- Iterate: Collect feedback, monitor compliance, and refine your policies for smoother deployment.
- Scale: Once tested, roll out the setup across your organization.
Best Practices for Microsoft Intune Management
Maximize the potential of Microsoft Intune with these best practices:
- Regular Policy Reviews: Update compliance and security policies to stay ahead of evolving threats.
- User Training: Ensure employees understand how Intune operates and its benefits for secure access.
- Utilize Conditional Access: Enforce policies based on real-time compliance checks.
- Monitor Performance: Use analytics tools to track device health and app usage.
- Automate Updates: Schedule automatic updates to minimize downtime and vulnerabilities.
Tips for Beginners
- Leverage Microsoft Documentation: Microsoft provides comprehensive guides and tutorials for each step of Intune setup.
- Use Templates: Intune offers built-in templates for compliance and configuration policies to save time.
- Start Small: Begin with one platform (e.g., Windows) before expanding to other device types.
- Enable Alerts: Set up notifications for critical events like policy non-compliance or enrollment failures.
Applications of Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Intune has broad applications in IT management, catering to various operational, security, and compliance needs. Below are its core applications:
1. Mobile Device Management (MDM)
Microsoft Intune allows businesses to manage a diverse range of devices, including Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android, ensuring comprehensive device management across platforms.
- Configure device settings remotely.
- Ensure compliance with company policies.
- Protect data on lost or stolen devices by performing remote wipes.
2. Mobile Application Management (MAM)
With Intune, organizations can manage and secure applications without requiring full device control.
- Deploy, update, or remove apps from users’ devices.
- Set app protection policies to safeguard corporate data.
- Control how corporate apps interact with personal apps.
3. Endpoint Security
Intune strengthens security by enforcing endpoint protection policies.
- Integrates with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to detect and respond to threats.
- Requires encryption on devices using BitLocker or FileVault.
- Enforces compliance with conditional access policies.
4. BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) Management
Intune supports BYOD environments, allowing employees to use their personal devices securely.
- Segregates personal and corporate data.
- Enables secure access to corporate apps and resources.
- Enables IT to manage corporate data remotely without affecting personal data on the device.
5. Zero-Touch Deployment
For corporate-owned devices, Intune simplifies deployment through automation.
- Configures devices out-of-the-box using Windows Autopilot or Apple Business Manager.
- Reduces IT workload by pre-configuring settings, apps, and security policies.
6. Compliance and Policy Enforcement
Intune helps organizations ensure their devices and apps comply with internal and regulatory requirements.
- Define compliance policies for devices and apps.
- Block access to corporate resources for non-compliant devices.
7. Unified Endpoint Management (UEM)
As part of Microsoft Endpoint Manager, Intune delivers seamless management for both cloud-based and on-premises devices, streamlining IT operations.
- Manage desktops, mobile devices, servers, and IoT endpoints.
- Streamline operations by combining Intune with Configuration Manager.
Use Cases for Microsoft Intune
1. Securing Remote Workforces
In the age of hybrid and remote work, Intune plays a critical role in maintaining security and productivity.
- Securely deploy resources, such as VPNs, apps, and Wi-Fi configurations, to remote employees.
- Ensure devices meet security policies before accessing corporate networks.
- Enable remote troubleshooting and support through dashboards.
2. Supporting BYOD Policies
Organizations implementing BYOD policies leverage Intune to balance security and user flexibility.
- Allow employees to work from personal devices while safeguarding corporate data.
- Restrict copying, sharing, or printing of sensitive information from unmanaged devices.
- Manage app permissions for personal devices using app protection policies.
3. Compliance with Industry Standards
Intune helps businesses in regulated industries maintain compliance with strict security requirements.
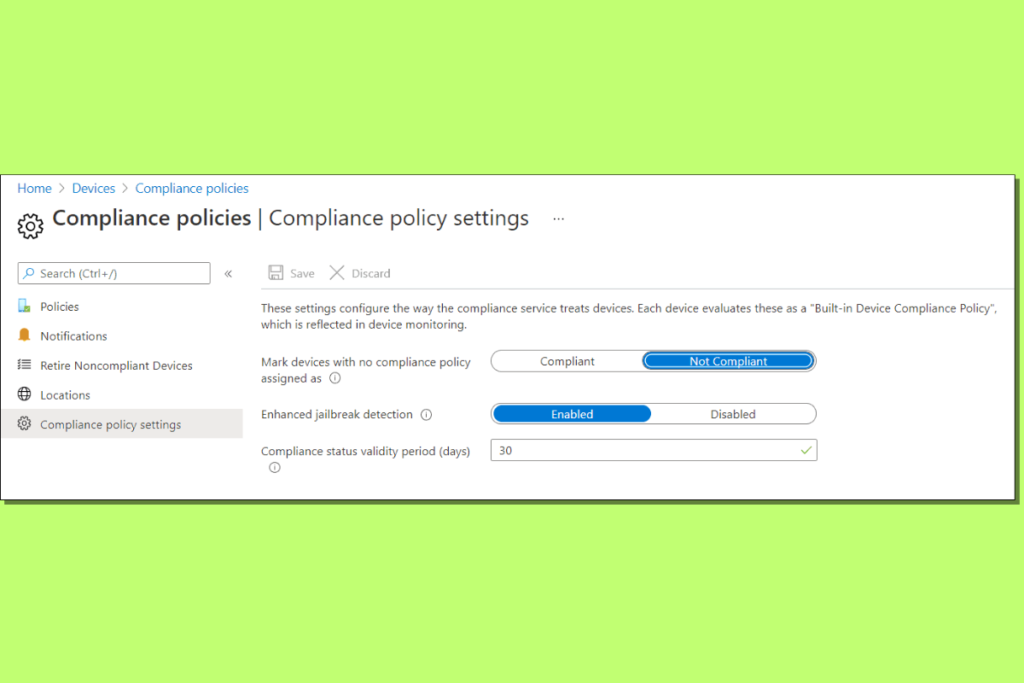
- Enforce encryption and password policies for devices storing sensitive information.
- Generate compliance reports for audits.
- Meet industry-specific standards like HIPAA for healthcare or GDPR for data privacy.
4. Simplifying Device Lifecycle Management
From onboarding to retirement, Intune simplifies the management of corporate-owned devices.
- Automate initial setup with pre-configured profiles.
- Monitor device performance and apply updates remotely.
- Wipe or reset devices when they are retired or reassigned.
5. Enhancing Education Environments
Schools and universities utilize Intune to streamline device management for students and educators.
- Distribute learning apps and tools efficiently.
- Ensure compliance with privacy and security standards for student data.
- Manage shared devices in classroom settings with ease.
6. Strengthening Retail Operations
Retailers use Intune to manage devices like point-of-sale systems, tablets, and kiosks.
- Ensure secure and reliable operation of customer-facing devices.
- Manage access to retail applications and inventory systems.
- Update and troubleshoot devices remotely to minimize downtime.
7. Healthcare Device Management
Healthcare organizations rely on Intune for managing devices while ensuring patient data security.
- Secure devices used to access Electronic Health Records (EHR).
- Implement app protection policies to prevent data leaks.
- Ensure compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA.
8. Optimizing Financial Services
Financial institutions leverage Intune for secure and compliant device management.
- Enable remote work for financial advisors without compromising data security.
- Protect sensitive customer information with strict app and device policies.
- Monitor compliance and generate reports for regulatory audits.
9. Enabling Secure Application Access
Organizations can use Intune to provide secure access to corporate apps and resources.
- It also enables organizations to restrict access to corporate resources based on device compliance and user roles, enhancing security and control.
- Manage access permissions dynamically with conditional access policies.
- Enable multi-factor authentication for enhanced security.
10. Facilitating IoT Device Management
Intune extends its capabilities to Internet of Things (IoT) devices, making it ideal for industries using smart devices.
- Secure IoT endpoints in manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.
- Monitor and control device configurations remotely.
- Integrate IoT device management with other enterprise IT systems.
Why Choose Intune for Your Business?
- Scalability: Manage devices and users in organizations of all sizes, from SMBs to enterprises.
- Cross-Platform Support: Intune supports Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android, providing unmatched versatility.
- Integration: Seamlessly integrates with Microsoft 365, Azure AD, and Defender for Endpoint.
- Ease of Use: Intune’s intuitive dashboard and automation features simplify IT management.
Conclusion
Microsoft Intune stands out as a game-changing solution for modern device and application management. Whether you’re securing BYOD environments, deploying company-owned devices, or managing compliance, Intune simplifies the process while enhancing organizational security. Its integration with Microsoft’s powerful ecosystem ensures flexibility, scalability, and seamless user experiences—making it the go-to tool for businesses worldwide.
Investing in Microsoft Intune means investing in a future-proof solution for IT management that balances user productivity with robust security measures.
FAQs
1. What platforms does Microsoft Intune support?
Microsoft Intune supports a wide range of platforms, including Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android devices.
2. How does Microsoft Intune ensure data security?
Intune secures data through features like encryption, conditional access, compliance policies, and the ability to remotely wipe corporate data from lost or stolen devices.
3. Is Intune capable of managing both personal and corporate devices?
Yes, Intune supports both BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) and corporate-owned devices, providing secure management and data segregation.
4. Is Microsoft Intune suitable for small businesses?
Absolutely! Intune’s flexible pricing and scalable features make it a great choice for businesses of all sizes.
5. What’s the difference between Intune and Microsoft Endpoint Manager?
Intune is a part of Microsoft Endpoint Manager, which combines Intune’s cloud-based device management with Configuration Manager’s on-premises capabilities for a unified endpoint management experience.


Leave a Reply